Cavitations in the Jawbone
The hidden dangers of chronic jawbone inflammation (also known as FDOK/NICO)
Chronic inflammatory areas in the jawbone can develop wherever teeth have been extracted — especially wisdom teeth — as well as around root canal-treated teeth or incompletely developed wisdom teeth. In many cases, particularly with wisdom tooth extractions, the body was not adequately prepared for the surgical procedure and was unable to heal properly after the often invasive operation.
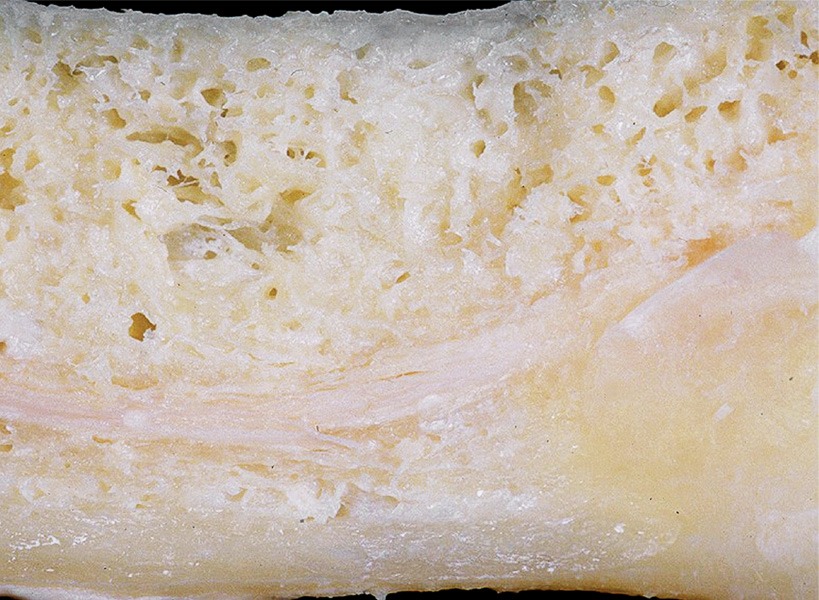

Healthy bone
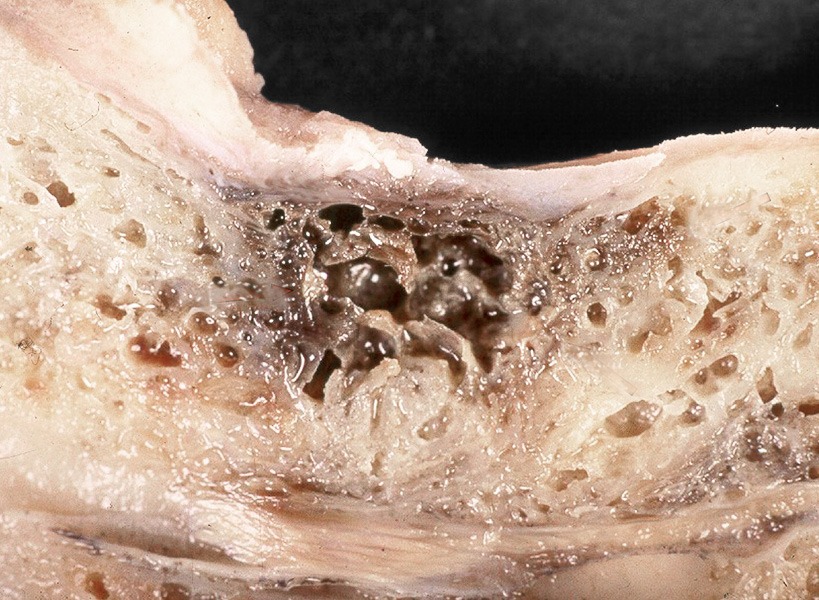
Diseased bone
Similar to what can occur in root canal-treated teeth, these areas can produce toxic substances and inflammatory signaling molecules (cytokines) such as TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, or RANTES. These substances can have systemic effects and trigger a wide range of symptoms —commonly associated with so-called cavitations (FDOK/NICO) are neurological symptoms, joint and skin issues, thyroid dysfunction, and chronic gastrointestinal problems. If left untreated, cavitations can silently burden the entire body for years, initiating or perpetuating chronic inflammatory processes. This is why it is so important to identify and treat them holistically.
Diagnosis
Cavitations can be reliably diagnosed using digital 3D volume tomography (DVT) if suspected. These scans are carried out during your initial examination at our practice.
Please note: Only specially trained practitioners with experience in the field of biological dentistry and cavitations are able to correctly identify and treat these pathological changes.
In individual cases, we also use the CaviTAU®ultrasound device, which provides us with precise information on bone density without radiation exposure. This method is a valuable addition to CBCT and provides additional information for assessing the jawbone and planning treatment.
Therapy – Surgical removal of cavitations
Chronic inflammatory bone areas are treated by cleaning them in a minimally invasive surgical procedure using modern piezo surgery. This technique enables very precise treatment that is gentle on the tissue and does not damage surrounding structures.
The cleaned wound is subsequently disinfected with ozone. In our practice, the treated area is then filled with PRF membranes (platelet rich fibrin). This intelligent, biological material is obtained from the patient’s own blood and is therefore completely natural and biocompatible. This procedure uses the body’s own healing mechanisms: When tissue is injured, the body produces special proteins that accelerate the wound healing process. The PRF membranes stimulate bone and tissue regeneration, promote natural healing and make a significant contribution to the stability and regeneration of the jawbone.
Depending on the extent of the cavitation, we also use human, protein- and DNA-free bone substitute material to reconstruct the defects in a stable manner and create optimal conditions for healing.
As always, there is more to holistic healing than surgery
Surgical measures are not the only decisive factor for sustainable regeneration after cavitation removal – a targeted diet (Food Design Concept), lifestyle and a targeted supply of micronutrients (Bone Healing Protocol) play a key role. Only an optimally nourished body can heal effectively, regulate inflammation and build new, healthy tissue.
Further information, including helpful videos and specific recommendations, can be found on our website in the Lifestyle & Nutrition, Micronutrients and Healing & Regeneration sections.
Photos: J Oral Pathol Med 1999; 28:423.
